Build an Interchain Dapp with Axelar - Part 1
You can find the complete code for this tutorial on GitHub.
Currently, Web3 development primarily centers around deploying a smart contract to one chain at a time, and in the future, these contracts will be deployed to multiple chains simultaneously.
Moralis offers industry-leading tools that make interchain Web3 development more accessible for millions around the world. Let’s build a Moralis dapp that integrates with Axelar to send interchain transactions.
Develop a Smart Contract
In part 1, you will write a smart contract that transfers an ERC-20 token along with a GMP message between the Ethereum and Polygon blockchains.
In part 2, you will connect that smart contract with a frontend application built with Moralis and WAGMI.
Prerequisites
This tutorial uses Hardhat for Visual Studio Code with command-line completion to write a smart contract in Solidity. If you haven’t used Hardhat before, run through Harhat's Getting Started tutorial first.
Clone the Smart Contract Starter Code
Clone the Gmp-Distribution starter code from GitHub. You should be able to see the following files:
contracts/GMPDistribution.sol— Sets up an empty contract calledGMPDistribution.chains.json— Contains relevant information about the blockchains you’ll deploy the smart contract on.hardhat.config.ts— Contains the configuration of the blockchains that you can interact with via Hardhat.scripts/deploy.ts— A script that will deploy the smart contract.
Install Dependencies
Run npm install for all the dependencies needed to compile the contract.
Set Up Axelar Services
To send an interchain transaction with Axelar, you’ll need the following contracts:
AxelarExecutable– The contract to handle a message on the destination chain once a transaction has been sent to the Axelar network.IAxelarGateway– The Axelar Gateway smart contracts.IAxelarGasService– The Axelar gas service.IERC20– The ERC-20 token interface to access ERC-20-related functionality.
Install these dependencies into Gmp-Distribution via the Axelar-GMP npm package. Once they have been installed, import them into contracts/GMPDistribution.sol in the starter code:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import { AxelarExecutable } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/executable/AxelarExecutable.sol";
import { IAxelarGateway } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/interfaces/IAxelarGateway.sol";
import { IAxelarGasService } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/interfaces/IAxelarGasService.sol";
import { IERC20 } from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract GMPDistribution {}
The contract must also inherit from AxelarExecutable to handle messages.
// imports
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {}
After importing, set the addresses for these contracts in the GMPDistribution contract’s constructor.
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
// Imports
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
IAxelarGasService public immutable gasService;
constructor(
// Set address for contracts in the constructor.
address _gateway,
address _gasService
) AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {
gasService = IAxelarGasService(_gasService);
}
}
Send Tokens
Now that Axelar services have been set up in the constructor, you’ll need a function that triggers the interchain transaction from the source chain. Since this function sends tokens and messages to many chains, call it sendToMany().
Set Up the sendToMany() Function
sendToMany() will need the following parameters:
_destChain– The name of the destination chain._destContractAddr– The address the transaction is being sent to on the destination chain._destinationAddrs– The list of addresses that will be receiving the ERC-20 tokens once on the destination chain._symbol– The symbol of the ERC-20 token being transferred._amount– The amount of ERC-20 tokens being transferred.
Mark this function as payable, since some native funds will need to be sent along with the function call to handle gas payment.
function sendToMany(
string memory _destChain,
string memory _destContractAddr, address[] calldata _destinationAddrs, string memory _symbol,
uint256 _amount
) external payable {}
Add Function Logic
Now you can add logic to sendToMany(). The function will need to do the following:
- Get the address of a token from its symbol.
- Send funds to another address.
- Approve the gateway to spend funds.
- Encode the recipient addresses on the destination chain to ensure that they are
bytes, since GMP messages must be of this type.
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
// Imports
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
IAxelarGasService public immutable gasService;
constructor() AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {}
function sendToMany(
string memory _destChain,
string memory _destContractAddr,
address[] calldata _destinationAddrs,
string memory _symbol,
uint256 _amount
) external payable {
// Check that funds have been sent. If no
// funds have been sent, revert the transaction.
require(msg.value > 0, "Gas payment required");
// Use the gateway contract to obtain the address
// of the ERC-20 token you will be sending from
// chain A to chain B.
address tokenAddress = gateway.tokenAddresses(_symbol);
// Transfer the ERC-20 token from the sender's
// wallet to this contract.
IERC20(tokenAddress).transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), _amount);
// Grant approval to the gateway contract to
// transfer funds on this contract's behalf.
IERC20(tokenAddress).approve(address(gateway), _amount);
// Encode and send a GMP message along with the
// token. _destinationAddrs is a list that contains
// the addresses of the ERC-2O token's final
// recipients once the transaction has arrived
// at the destination chain.
bytes memory recipientAddressesEncoded = abi.encode(_destinationAddrs);
// Output: a list of addresses in bytes
}
}
Once sendToMany() is called, the contract will be in control of the ERC-20 tokens you wish to send between chains. Before you can send the funds, though, you must implement the AxelarGasService so that you can pay for the transaction.
Pay Gas Services
Add the gas payment code to the sendToMany() function. [payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken()](https://docs.axelar.dev/dev/general-message-passing/gas-services/pay-gas#paynativegasforcontractcallwithtoken) will be called on the source chain before calling the gateway to execute a remote contract.
The required parameters are:
_destChain– The name of the destination chain where gas funds will be needed._destContractAddr– The final destination address of the interchain transaction - on the destination chain.recipientAddressesEncoded– The encoded GMP message._symbol– The token symbol._amount– The token amount.msg.sender– The address to refund surplus gas to.
function payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken(
address sender,
string calldata destinationChain,
string calldata destinationAddress,
bytes calldata payload,
string calldata symbol,
uint256 amount,
address refundAddress
) external payable;
With payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken(), the payment of the entire interchain transaction will use the native token of the source chain. For example, if you were to transfer funds from Ethereum to Polygon, you would pay transaction costs in ETH. msg.value pays for the transaction.
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
// Imports
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
IAxelarGasService public immutable gasService;
constructor() AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {}
function sendToMany(
string memory _destChain,
string memory _destContractAddr,
address[] calldata _destinationAddrs,
string memory _symbol,
uint256 _amount
) external payable {
// Check that funds have been sent
// Obtain token address
// Transfer token
// Grant approval to gateway contract
// Encode GMP message
// Pay gas with the source chain's native token.
gasService.payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken{value: msg.value}(
address(this),
_destChain,
_destContractAddr,
recipientAddressesEncoded,
_symbol,
_amount,
msg.sender
);
}
}
Initiate the Transaction
Initiate the transaction with a call to the IAxelarGateway contract. [callContractWithToken()](https://github.com/axelarnetwork/axelar-cgp-solidity/blob/cc122010edb9e459b74a5f6e611fd42a75c3f560/contracts/AxelarGateway.sol#L167) causes this contract to emit an event once it executes. An Axelar relayer will pick up the event and begin the interchain transaction.
callContractWithToken() takes the same parameters as payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken(), excluding the refund address.
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
// Imports
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
IAxelarGasService public immutable gasService;
constructor() AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {}
function sendToMany(
string memory _destChain,
string memory _destContractAddr,
address[] calldata _destinationAddrs,
string memory _symbol,
uint256 _amount
) external payable {
// Check that funds have been sent
// Obtain token address
// Transfer token
// Grant approval to gateway contract
// Encode GMP message
// Pay gas with the source chain's native token
// Begin the interchain transaction.
gateway.callContractWithToken(
_destChain,
_destContractAddr,
recipientAddressesEncoded,
_symbol,
_amount
);
}
}
Check the Function Code
Now the sendToMany() function is complete. The contract should look like this:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import { AxelarExecutable } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/executable/AxelarExecutable.sol";
import { IAxelarGateway } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/interfaces/IAxelarGateway.sol";
import { IAxelarGasService } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/interfaces/IAxelarGasService.sol";
import { IERC20 } from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
IAxelarGasService public immutable gasService;
constructor(
address _gateway,
address _gasService
) AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {
gasService = IAxelarGasService(_gasService);
}
function sendToMany(
string memory _destChain,
string memory _destContractAddr,
address[] calldata _destinationAddrs,
string memory _symbol,
uint256 _amount
) external payable {
require(msg.value > 0, "Gas payment required");
address tokenAddress = gateway.tokenAddresses(_symbol);
IERC20(tokenAddress).transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), _amount);
IERC20(tokenAddress).approve(address(gateway), _amount);
bytes memory recipientAddressesEncoded = abi.encode(_destinationAddrs);
gasService.payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken{value: msg.value}(
address(this),
_destChain,
_destContractAddr,
recipientAddressesEncoded,
_symbol,
_amount,
msg.sender
);
gateway.callContractWithToken(
_destChain,
_destContractAddr,
recipientAddressesEncoded,
_symbol,
_amount
);
}
}
If you call sendToMany() at this point, you should be able to send ERC-20 tokens along with a GMP message to the Axelar network. Successful transactions should be visible on the Axelarscan block explorer.
Receive Tokens
Once a transaction has been sent to the Axelar network, it needs to be appropriately handled on the destination chain. To do this, the receiving contract must make use of the AxelarExecutable contract by overriding its _executeWithToken() method.
Set Up the _executeWithToken() Function
_executeWithToken() takes the following parameters:
- Two
calldatastrings representing the source chain and source address, which are defined in theAxelarExecutablecontract and not needed for this tutorial. _payload– The inbound GMP message coming through the Axelar network, encoded as abytesobject._tokenSymbol– The symbol of the sent token._amount– The amount that the second token is worth.
function _executeWithToken(
string calldata,
string calldata,
bytes calldata _payload,
string calldata _tokenSymbol,
uint256 _amount
) internal override {}
Add Function Logic
Now you can add logic to _executeWithToken(). Once the transaction has been received on the destination chain, the contract will have a list of addresses as encoded bytes, along with an ERC-20 token. The function will need to do the following:
- Decode the
_payload, parsing thebytesobject into a list of addresses. - Divide the tokens up between each recipient address.
- Transfer the tokens to each recipient.
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
// Imports
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
constructor() AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {}
function sendToMany() external payable {}
function _executeWithToken(
string calldata,
string calldata,
bytes calldata _payload,
string calldata _tokenSymbol,
uint256 _amount
) internal override {
// Decode the payload into a list of recipient addresses.
address[] memory recipients = abi.decode(_payload, (address[]));
// Get each token address.
address tokenAddress = gateway.tokenAddresses(_tokenSymbol);
// Divide up the tokens between each recipient
// on the list. Here, it's divided evenly.
uint256 sentAmount = _amount / recipients.length;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < recipients.length; i++) {
// Transfer the tokens to each recipient.
IERC20(tokenAddress).transfer(recipients[i], sentAmount);
}
}
}
Check the Completed Code
At this point, you have a completed contract that can send an ERC-20 token from one chain to another, along with an encoded GMP message. The contract can also parse the GMP message and transfer the funds to each address on the destination chain.
The finished code should look like this:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import { AxelarExecutable } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/executable/AxelarExecutable.sol";
import { IAxelarGateway } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/interfaces/IAxelarGateway.sol";
import { IAxelarGasService } from "@axelar-network/axelar-gmp-sdk-solidity/contracts/interfaces/IAxelarGasService.sol";
import { IERC20 } from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
contract GMPDistribution is AxelarExecutable {
IAxelarGasService public immutable gasService;
constructor(
address _gateway,
address _gasService
) AxelarExecutable(_gateway) {
gasService = IAxelarGasService(_gasService);
}
function sendToMany(
string memory _destChain,
string memory _destContractAddr,
address[] calldata _destinationAddrs,
string memory _symbol,
uint256 _amount
) external payable {
require(msg.value > 0, "Gas payment required");
address tokenAddress = gateway.tokenAddresses(_symbol);
IERC20(tokenAddress).transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), _amount);
IERC20(tokenAddress).approve(address(gateway), _amount);
bytes memory recipientAddressesEncoded = abi.encode(_destinationAddrs);
gasService.payNativeGasForContractCallWithToken{value: msg.value}(
address(this),
_destChain,
_destContractAddr,
recipientAddressesEncoded,
_symbol,
_amount,
msg.sender
);
gateway.callContractWithToken(
_destChain,
_destContractAddr,
recipientAddressesEncoded,
_symbol,
_amount
);
}
function _executeWithToken(
string calldata,
string calldata,
bytes calldata _payload,
string calldata _tokenSymbol,
uint256 _amount
) internal override {
address[] memory recipients = abi.decode(_payload, (address[]));
address tokenAddress = gateway.tokenAddresses(_tokenSymbol);
uint256 sentAmount = _amount / recipients.length;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < recipients.length; i++) {
IERC20(tokenAddress).transfer(recipients[i], sentAmount);
}
}
}
Test compile by running npx hardhat compile in the terminal.
Deploy the Contract
Now you’re ready to deploy GMPDistribution on two EVM chains! Make sure that your connected wallet has enough funds to pay for gas costs.
To deploy the contract, go to your terminal window and run the scripts/deploy.ts:
hh run scripts/deploy.ts
As output, you should see your contract address, which you can verify on your chosen blockchain explorer (Etherscan for Ethereum and PolygonScan for Polygon). You’ll need these addresses to integrate with a Moralis frontend.
`Polygon contract address: <YOUR_ADDRESS>`
`Ethereum contract address: <YOUR_ADDRESS>`
Test the Contract
Now that you’ve deployed the contract, test it using the Hardhat console to ensure that everything is working correctly.
Start the Hardhat Command-Line Interface
Open your terminal window and start up the Hardhat command-line interface by typing the following command:
hh console --network polygon
Get a Deployed Contract Instance
To get a deployed instance of the contract, you’ll need an ethers ContractFactory object. Since the contract is named GMPDistribution, type the following to get the factory:
const Contract = await ethers.getContractFactory("GMPDistribution")
Use ContractFactory to get a deployed instance of the contract itself by attaching the contract’s deployed address.
const contract = await Contract.attach("0x5974f055DE2dDEcc2f07F0dE999c72DD21738a04")
There should now be a live instance of the Polygon-based contract that you can interact with on the command-line interface.
Ensure That the Connected Wallet Meets Requirements
Before interacting with the newly deployed contract, the connected wallet and the original owner of the token being sent must provide an allowance for the GMPDistribution contract to handle tokens. Without this allowance, the transferFrom() function in sendToMany() will revert.
You will be sending an aUSDC token, so you’ll need some in your wallet for the following to work. If you do not have any aUSDC tokens, you can get from Axelar’s faucet.
The [approve()](https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-contracts/blob/4e419d407cb13c4ebd64d3f47faa78964cbbdd71/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol#L132) function in the deploy.ts script is called to provide an allowance. This function takes two parameters:
spender– The address of the deployedGMPDistributioncontract.value– The amount of tokens to send. The following passes in a very large number for simplicity’s sake.
await aUSDCToken.approve(gmpDistribution.address, "1234567895");
This function is called on the ERC-20 token itself at the registered aUSDC address. There are many ways to interact with this contract including through Remix, the Hardhat console, or a script.
Call the sendToMany() Function
Now that the GMPDistribution contract is approved to send a very large number of tokens on our wallet’s behalf, call the sendToMany() function.
await contract.sendToMany(
"ethereum-2", // Destination chain
"0x1aa5E49bF5eC550Bccb72764731a60a9203aFD69", // Goerli contract address
["0x03555aA97c7Ece30Afe93DAb67224f3adA79A60f", "0xC165CbEc276C26c57F1b1Cbc499109AbeCbA4474", "0x23f5536D2C7a8ffE66C385F9f7e53a5C86F53bD1"], // Receiving addresses
"aUSDC", // Token symbol
6000000,
{value: "1000000000000000000"} // Amount of tokens to be sent
)
Once this function is called, the Hardhat console should return the transaction hash.
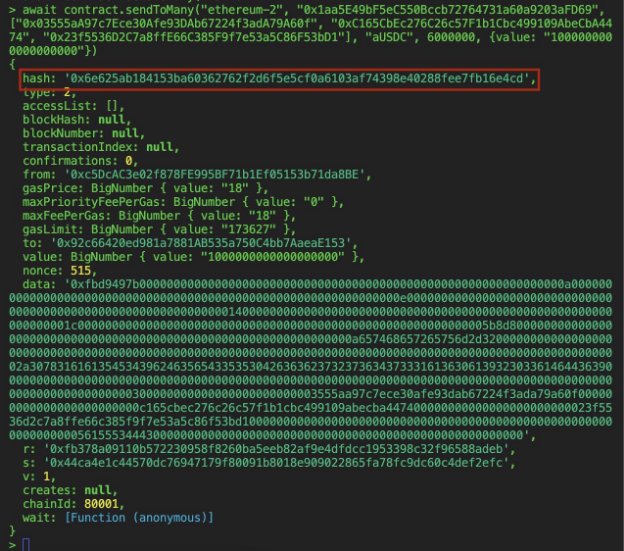
Check Results on Axelarscan
Put the transaction hash returned by the Hardhat console into Axelarscan to see it taking place.
The following screenshots show an example of a successful transaction:
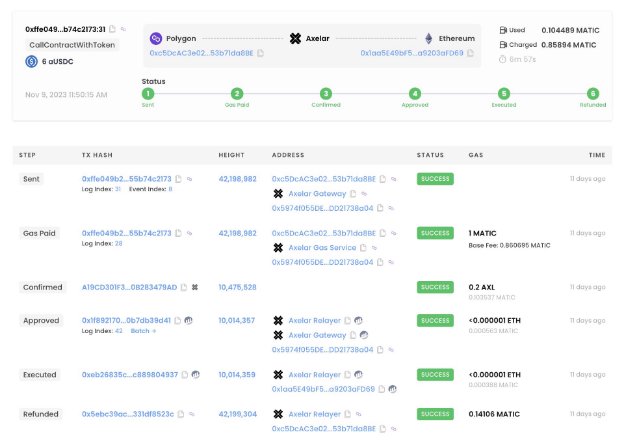
The following screenshots show an example of a successful transaction:
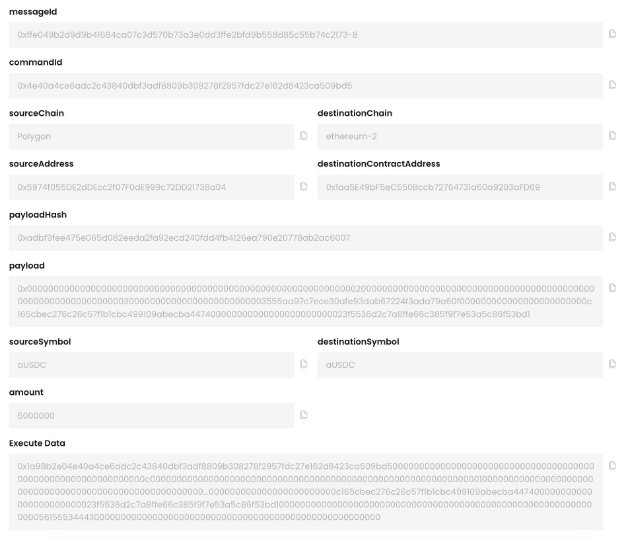
Next: Connect to the Frontend
So far, we’ve written a Solidity-based contract and deployed it on Ethereum and Polygon. In part 2 of this tutorial, we’ll build a dapp frontend with NextJS, a ReactJS framework.